Article by Hans Holter Solhjell.
Published September 15th. 2020.
Part 1 of a series of articles about the response funnel.
You can read part two of the article about The Response Funnel here.
The Response Funnel Model is now also translated into more languages.
Please see this page for a complete list of languages.
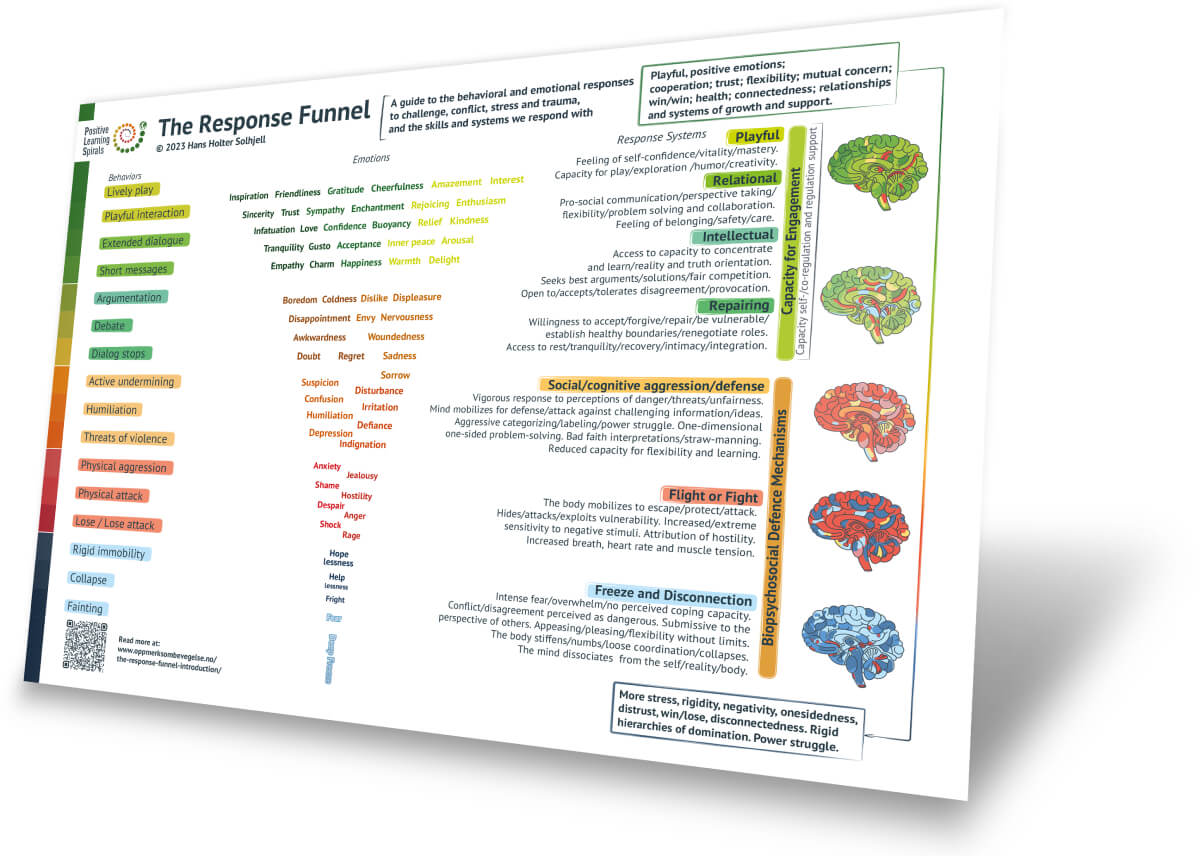
The response funnel model provides a overview of a wide range of ways we respond behaviorally to challenges, conflict, crisis and stress.
The model was developed in the context of caregiver-child relationships and developmentally supportive conflict resolution, in families, kindergartens and schools. Furthermore it can also be relevant and adapted to other contexts.
The model is inspired by and based on 25 years of interest in research, theories, practical methods and work in fields such as stress, trauma, child-development, parenting, communication, conflict resolution, crisis management, self-development, embodiment, therapy, martial arts and self-defense. As well as systems theory, integral philosophy, education, educational design etc.

Download The Response Funnel model here!
The Response Funnel is a new and innovative model in the field of trauma, conflict resolution, relationships, and self-development.
To receive information about The Response Funnel please register for our newsletter. You will then receive a free copy of The Response Funnel.
Purpose and potential uses of the model
Teaching tool
The first intention is as a teaching tool, to teach, explain and give an overview of various responses and behavioral options related to stress, trauma, relationships, conflict, conflict resolution, crisis-response, self-development, parenting, self-regulation and regulation-support.
It is meant to give a broad overview of some of the responses we have available to us when we experience challenges, conflict, or stress. The model focuses on both more spontaneous, positive or negative, behaviour, but also and more importantly on learnable solution-oriented regulation-supportive behaviours and relational skills.
Some of the responses are more impulsive in nature, and others require focused learning, practice and maturation to acquire. Importantly, the demands, complexity and stress of various situations varies, so skills that are easy to use in one situation might be difficult to use in another situation.
Supporting and motivating regulation-capacity development
The second purpose of the model is to support and motivate the development of a broad skill set, and to expand ones capacity to regulate our states and behavior. And to help promote the health of both oneself, our immediate relationships and our circles of influence.
This includes developing emotional and behavioral granularity, our ability to differentiate between different emotions and feelings, and relational actions. Further, to expand capacity to accept and be comfortable with disagreement and debate, and accept conflict, discomfort, pain, stress and negative emotions to a certain degree. And to gradually be able to deal with more challenging, complex and stressful situations.
Self-reflection tool
The model is also meant to be a self-reflection tool – We can use the graphic to explore and reflect on our own response patterns and skills, as well as consider what skills we might want to focus on for capacity development.
In a specific relationship, or in a particular situations, do I tend to end up on the lower levels of the scale, arguing, undermining or further down on the scale? Where do I feel comfortable or not? With debate, dialogue or play? Can I develop more capacity for dialogue, or play?
The ultimate goal of the model is to inspire, support, and motivate in the development of, as well as a repair of, capacity for self and co-regulation, and regulation-support.
The model can also be used to explore where we might need additional support from a partner, friends, family, learning partner, coach, teacher, or therapist.
For partners, teams, and organizations it can also be used to explore our capacity as a group, team or family, where one as group members have complementary skills, how one can support each other better, and benefit from the variation of skills. And which capacities and skills, like healthy debate, dialogue or playfulness skills, one would benefit from having more of in the group.
Both for individuals as well as groups, honestly and accurately appreciating and accepting both ones strengths as well as our weaker areas is seen as valuable and important for further capacity building.
The response funnel model can also be helpful to track our development over time. We can then do this on a regular time interval, like a month, quarterly, half-year or yearly schedule, to keep track of your learning or therapy process.
Some points to note about the response funnel model
Funnel metaphor
The visual metaphor of a funnel is used to illustrate that our capacity for learning, conflict resolution and behavioural and cognitive flexibility, in general and broadly speaking, is reduced as stress and feelings of threat, unsafety and negative emotions increase. Òur capacity, is, by and large, higher higher up in the funnel.

Many variations and exceptions
The illustration of the funnel places the positive emotions at the top, and gradually more negative emotions further down. This is not meant to indicate that positive emotions are always better for all purposes, or a ranking of emotional experiences as such.
Emotions, and life, are complex, and emotions has varied and complex effects on many aspects of our behaviour, thinking, problem solving, awareness and decision making. For instance, some unsafety and anger might make one more ready to act decisively, additaionally some negative emotion have been shown to be better for rational decision making compared to more positive emotion.
Individual response in relational, social, group, organizational and cultural context
The response funnel model primarily maps one individual’s response options, possibilities, and limitations. It is also meant to support the capacity development of individuals, long term safeguarding of our capacity, as well as repair of capacity limitations due to injury or trauma.
It is important to point out that even with this individual oriented focus, the model is meant to be used in a context that emphasize the importance of our circumstances as well as our responsibility, on an individual as well as systemic level, towards each other.
Importantly, the model was originally developed in the context of caretaker-child conflict, with the aim of explaining the importance of co-regulation and regulation-support for the developing child.
Moreover, the model, influenced by Bronfenbrenner’s ecological systems theory and systems theory in general, sees our capacity as individuals as greatly influenced by our immediate as well as long term contexts, in close relationships, wider social groups, organizations, cultural, political and legal contexts. As well as our natural, local as well as global, natural environment.
You can read part two of this article about The Response Funnel here.
You can download a basic version of the response funnel here.
Register for our newsletter and receive a copy of The Response Funnel.
If you are interested in more information about the response funnel model you can register for our newsletter. You will then receive a copy of The Response Funnel.
In our newsletter, you will receive information about new developments of The Response Funnel as well as our related courses and training programs.
Global Response Funnel Translation Project
Do you want to participate in the Global Response Funnel Translation Project, and help translate the model? Please read more about the project here.